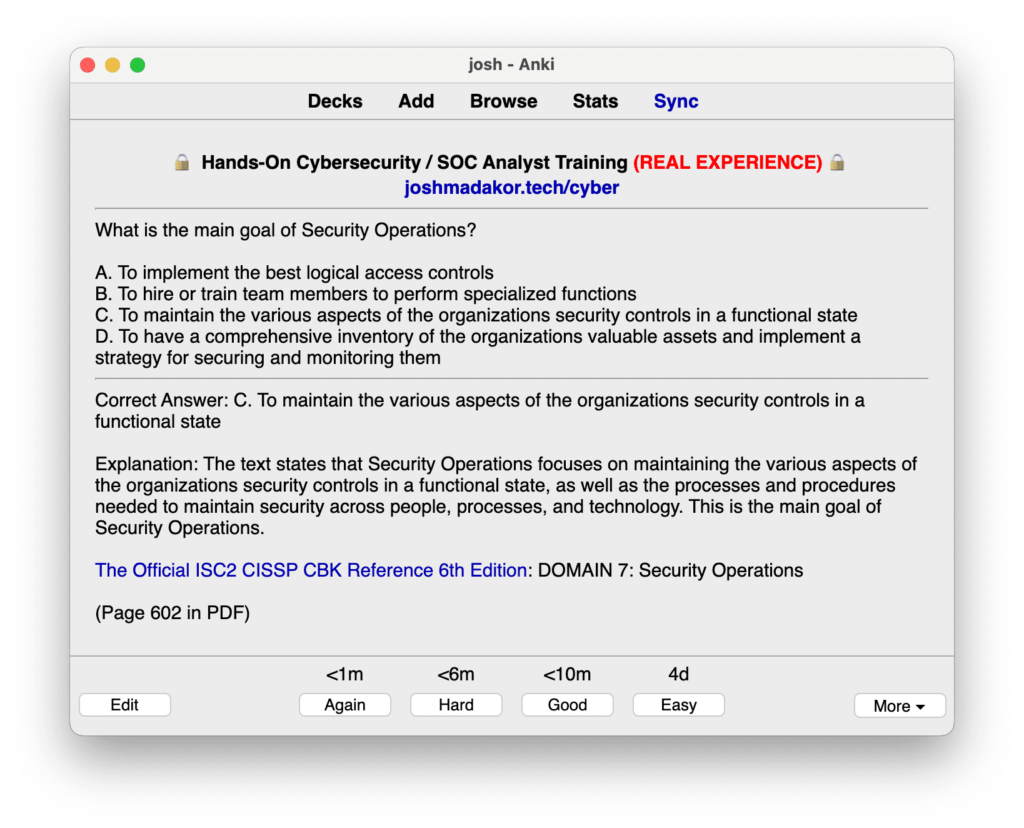
🔒 Hands-On Cybersecurity Course + INTERNSHIP 🔒
DOMAIN 7: Security Operations – A Comprehensive Overview for the CISSP Practice Exam
Preparing for the CISSP Practice Exam is a critical step in advancing your cybersecurity career. Especially, mastering Domain 7: Security Operations is essential. This domain, a significant part of the CISSP exam, covers the foundational elements and advanced concepts in security operations. Let’s delve into what this entails.
Understanding the Core of Security Operations
At its heart, Domain 7 focuses on the day-to-day management and protection of information systems within an organization. This includes understanding and applying foundational security operations concepts, which are crucial for the “CISSP Practice Exam.” The domain encompasses various aspects, such as resource protection techniques, incident handling, and understanding the role of forensic analysis in security operations.
Key Aspects of Domain 7
- Resource Protection Techniques: It’s vital to understand the methods and strategies used to protect physical and digital assets. This includes access control mechanisms, security mechanisms for personnel, and the secure management of physical resources.
- Incident Management and Response: A significant part of Domain 7 in the “CISSP Exam” involves preparing for and managing security incidents. This includes understanding incident handling processes, developing response strategies, and learning the importance of timely responses.
- Forensic Analysis: Here, you’ll learn about the principles and practices of forensic analysis as part of the security operations. This knowledge is crucial for the “CISSP Practice Exam,” helping you understand how to gather and analyze evidence following security incidents.
Optimizing Your CISSP Exam Preparation
To effectively prepare for the “CISSP Practice Exam,” especially Domain 7, it’s recommended to engage with various learning materials and practice tests. These resources provide a practical understanding of the domain and prepare you for the types of questions you’ll encounter in the CISSP Exam.
Further Insights into Security Operations
Security operations, a critical aspect of information security, encompasses a range of practices and principles designed to protect an organization’s information assets. Understanding these concepts is not just crucial for certification exams but also for practical, real-world application.
1. Security and Risk Management
Security operations begin with a deep understanding of risk management. This involves identifying potential security threats and vulnerabilities, and then implementing strategies to mitigate these risks. It includes the development of security policies, standards, and procedures that guide the operation of security measures within the organization.
2. Asset Security
Protecting an organization’s assets is a cornerstone of security operations. This not only includes digital assets like data and network resources but also physical assets like servers and workstations. Asset security involves classifying information and resources, ensuring appropriate levels of protection, and managing the data lifecycle from creation to disposal.
3. Network and Communications Security
A significant part of security operations is ensuring the security of the organization’s network and communications systems. This includes the implementation and management of network security controls, monitoring network traffic to detect and respond to anomalies, and ensuring secure communication channels.
4. Identity and Access Management
Controlling who has access to what information is vital in security operations. This includes managing user identities, establishing robust authentication mechanisms, and controlling access to resources based on user roles and responsibilities. This process ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information.
5. Security Assessment and Testing
Regular assessments and testing of security measures are crucial to ensure they are effective and up to date. This includes conducting audits, vulnerability assessments, and penetration testing to identify and address potential security gaps.
6. Security Incident Management
A proactive approach to security incident management is essential. This involves having a well-defined incident response plan, training staff to recognize and report incidents, and conducting regular drills to ensure preparedness. The goal is to minimize the impact of security incidents when they occur.
7. Continual Improvement
The field of security operations is ever-evolving, and continual improvement is key. This includes staying updated with the latest security trends and technologies, learning from past incidents, and regularly reviewing and updating security policies and procedures.
In summary, security operations cover a wide range of activities, all aimed at protecting an organization’s information assets. From risk management to incident response, each aspect plays a critical role in maintaining the security and integrity of an organization’s data and systems.
Conclusion
As you prepare for your “CISSP Practice Exam,” focusing on Domain 7: Security Operations is key. This domain not only enhances your knowledge of security operations but also equips you with the skills necessary to excel in the Domain 7 CISSP Exam.” Remember, understanding and applying these concepts is crucial for anyone aiming to succeed in the field of information security.